Note: If your server has a legitimate need to perform DNS recursion (example – you have applications that need to resolve external DNS), you can alternately disable and/or scope the local Windows Firewall rule that allows incoming DNS requests.
Windows 2003: Uncheck or remove any rules for DNS, DNS.exe or exceptions for port 53.
Windows 2008 and higher: You’ll want to disable or scope both DNS TCP and DNS UDP rules.
To disable DNS Recursion in Windows DNS:
-
Open DNS Manager (To open DNS Manager, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click DNS.)
-
In the console tree, right-click the applicable DNS server, then click Properties.
-
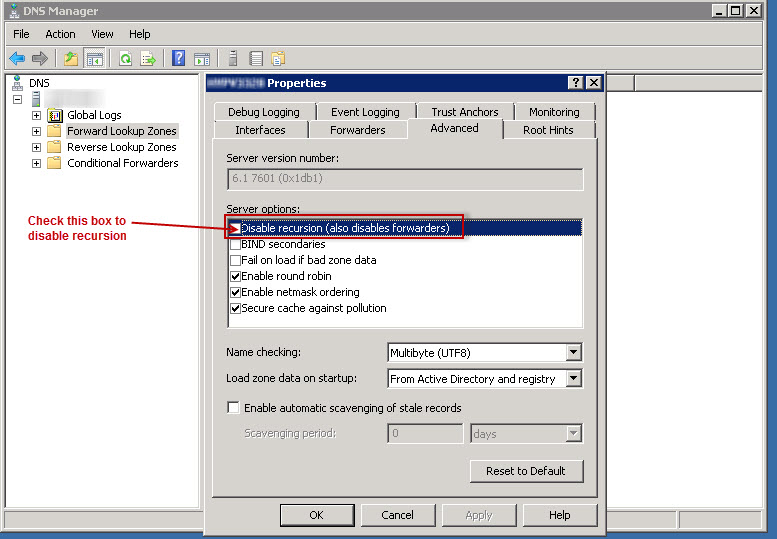
Click the Advanced tab.
-
In Server options, select the Disable recursion check box
-
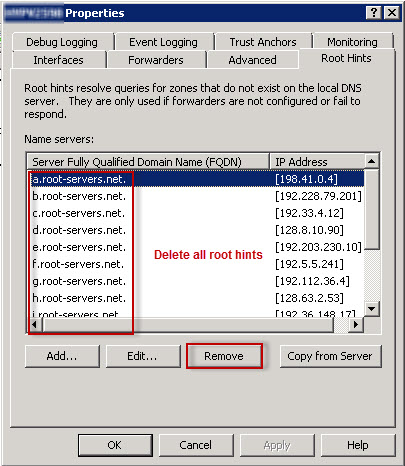
Under the Root Hints tab, delete all root hints entries, and then click OK.
-
Restart the DNS service (from the Services control panel)
How to disable recursion:
How to delete root hints:
For further reading:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc771738.aspx
Why DNS Recursion should be disabled for public access:
Content retrieved from: https://support.appliedi.net/kb/a1010/how-to-disable-recursion-on-a-windows-dns-server.aspx.
